
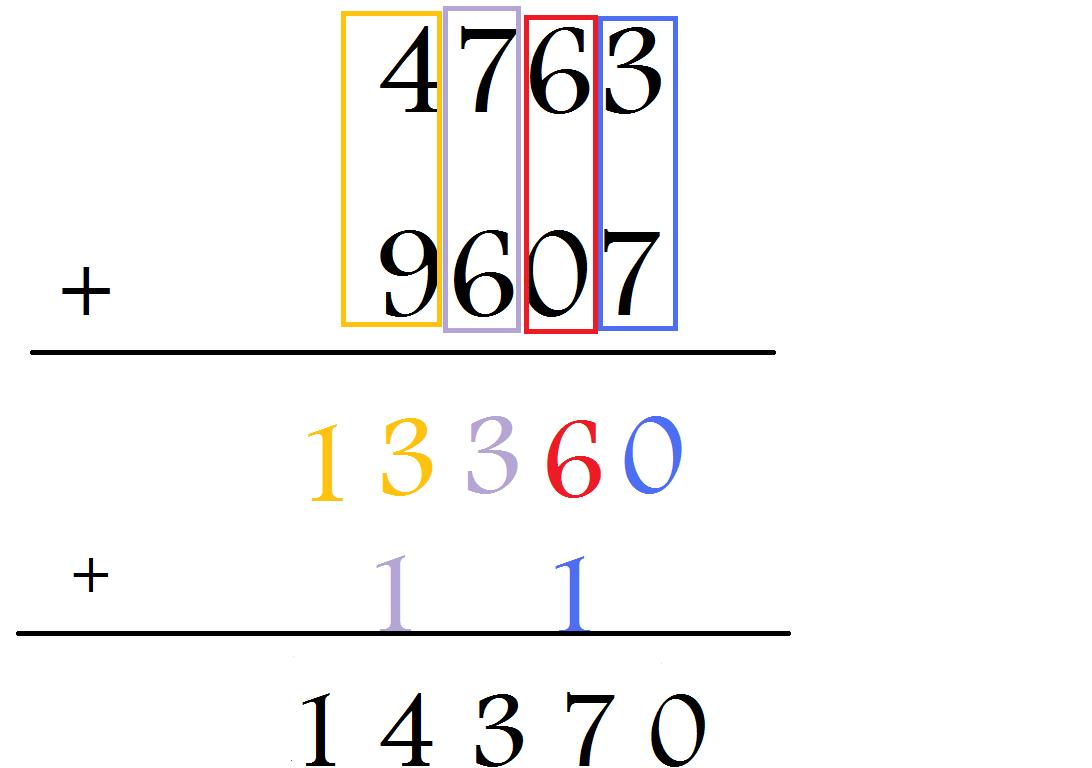
Step four: Again, we continue the same process by adding the digits in the next column, which is the hundreds place. We now write the 2 in the tens place and carry the 1 up to the hundreds place.

It is important to recognize that although we have added up 1 + 7 + 4 to get 12, what we have really added is 10 + 70 + 40 to get 120. Again, we will need to regroup since we have a 2 digit number. In this case, we add 1 + 7 + 4, which equals 12. Step three: Continue the process by adding the digits in the tens place next. Since 10 has two digits (1 ten and 0 ones), we write the 0 in the ones place and we carry the 1 (which represents 1 ten) to the tens place in the next column. In this example, we add 8 + 2, which is 10. Once you add the two digits, place the sum underneath the line, also in the ones place. Step two: Start by adding the two digits in the ones places. See how we set up the standard algorithm with the example 378 + 542. If one number has more digits than the other, that number should go on top. Step one: Line up the digits of each addend by place value. The standard algorithm of addition goes as follows: Note that for the addition and subtraction examples, regrouping is needed and shown. Read through those steps below alongside an example of each one in action. The standard algorithm for each operation follows a specific set of steps. Note: Not all states follow the same math standards.
This sets the foundation of the concept before students move on to the standard algorithm in the next grade. It is important to note that for each of these standards, the previous grade level standard focuses on teaching strategies for the respective operation based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between the inverse operation.

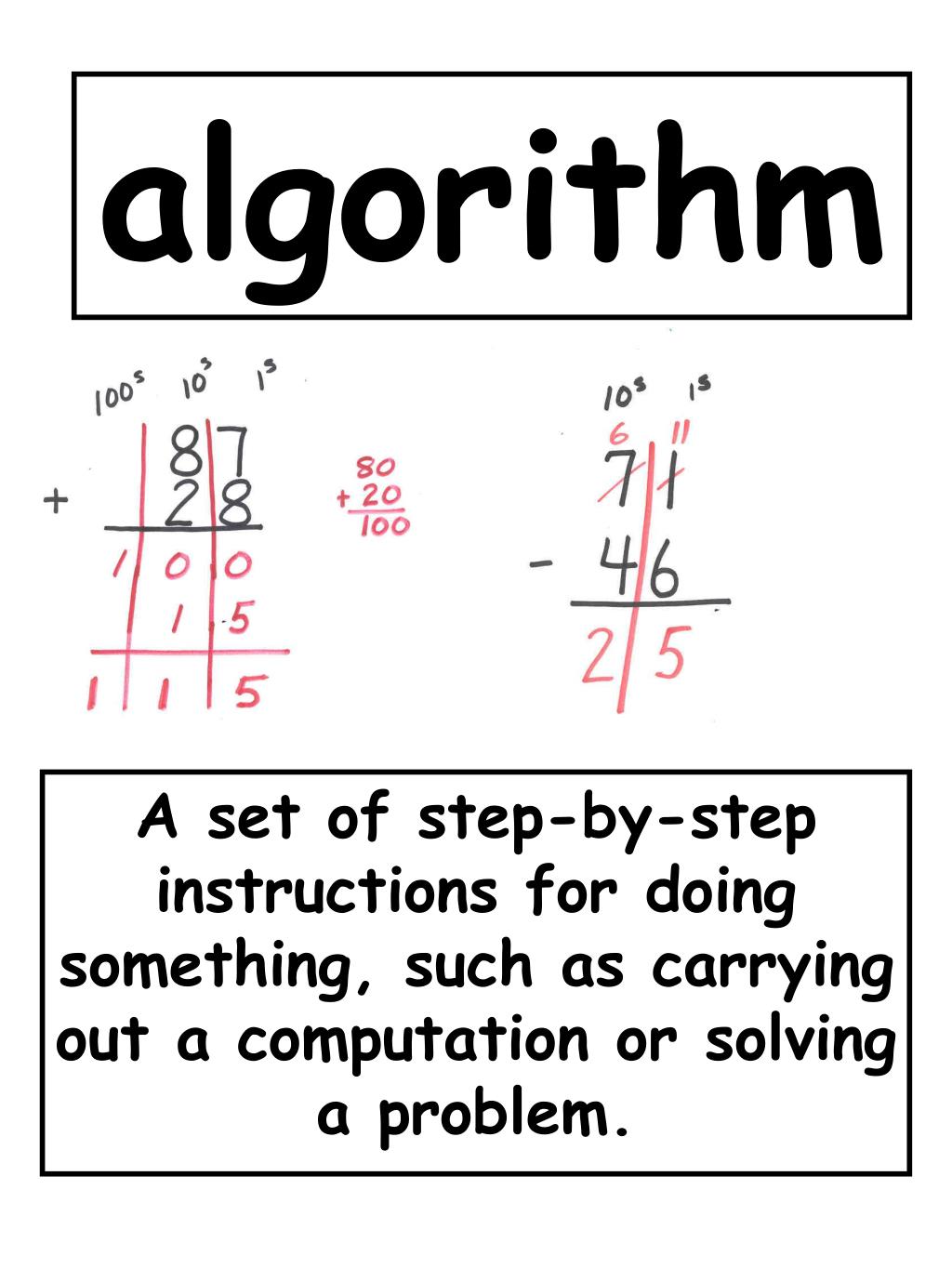
It is extremely important for students to have the conceptual basis of the operation they are performing before they begin to learn the standard algorithm for each operation. The CCSS introduces the standard algorithm of division, also known as long division, in 6th grade. In 5th grade, students are introduced to the standard algorithm of multiplication, and will learn strategies similar to the standard algorithm of division, such as the partial quotients model. In 3rd grade, students are expected to fluently add and subtract within 1,000 using strategies and algorithms, and then add and subtract within 1,000,000 using the standard algorithm in 4th grade. In 2nd grade, however, it is possible that students will be introduced to the standard algorithm of addition and subtraction with small numbers. The word “algorithm” is first mentioned in the Common Core State Standards in grade 3. When do students learn the standard algorithm? This is extremely important for all operations and their algorithms. In this context, the process is addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division of multi-digit numbers.įor example, addition using the standard algorithm looks like this:īefore learning the standard algorithm as shown in this example, students should already have the conceptual basis of addition and regrouping, as this is simply a quicker, neater process for performing the operation.
SIMPLE MATH ALGORITHM EXAMPLE DOWNLOAD
Download Free Now! What is a standard algorithm?Ī standard algorithm is a set of steps to complete a process.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
